SAMPLE LESSONS > A LEVEL GRAVITATIONAL FIELD
WEIGHTLESS
For maximum learning experience, download the notes and watch the video lessons.
Remember to scroll down for in-depth learning via the worked examples.
WORKED EXAMPLES
EASY 1
An astronaut in a spaceship orbiting the Earth experiences “weightlessness” because
A |
His reaction force is equal and opposite to his weight. |
B |
He has zero weight. |
C |
His weight is the only force acting on him. |
D |
The gravitational field strength at the location of the spaceship is negligible. |
Answer
EASY 2
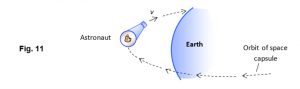
An astronaut is riding in a space capsule in a circular orbit about the Earth at a constant speed as shown in Fig. 11.
The resultant force on the astronaut is
A |
zero as the astronaut experience weightlessness. |
B |
equal to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the seat on the astronaut. |
C |
less than its weight and is equal to the between its weight and the normal force exerted by the seat on the astronaut. |
D |
the gravitational force on the astronaut. |
Answer
EASY 3
Assuming the Earth to be a uniform sphere rotating about an axis through the poles, the weight of a body at the Equator compared with its weight at a pole would be
A |
greater, because the angular velocity of the Earth is greater at the Equator than at a pole |
B |
greater, because the weight at the Equator is given by the sum of the gravitational attraction of the Earth and the centripetal force due to the circular motion of the body |
C |
the same, because the weight is the gravitational attraction of the Earth and for a uniform sphere, even when rotating, this is independent of the body’s position on the Earth |
D |
smaller, because the gravitational attraction of the Earth must provide both the weight and the centripetal force due to the circular motion of the body |
E |
smaller, because the gravitational attraction at the pole is greater than that at the Equator |
Answer
EASY 4
An object in a space capsule orbiting the Earth seems to be floating.
Which statement describes the forces acting on the object?
A |
There are no forces on the object |
B |
The centrifugal force on the object is equal and opposite to its weight |
C |
The centripetal force on the object is equal and opposite to its weight |
D |
The weight of the object is the only force acting on it |
Answer
The lessons and resources above are just the tip of the iceberg.
Nothing is better than tasting Physics Academy’s live lessons & accessing the full version of our digital resources. Sign Up for a FREE Trial Class & Experience the Best Physics Lesson Yourself!
START YOUR FREE TRIAL

Mr. Bryan Lai
FOUNDER OF PHYSICS ACADEMY
Over the past 15 years, my students remember me as the “Go-To” Master Physics Tutor who has consistently helped over 1,280 students achieved Distinctions for Secondary & JC A Level in just 6-9 Months, regardless of their current exam grades.
All thanks to my Physics Prof Learning System which allow students to learn Physics 24/7 anytime, anywhere! By combining Weekly Classroom Lessons, Digital Lessons, Physics Compendium (AKA Physics Bible), and FREE Consultations. I’ve helped my students clarify all their doubts & skyrocket their results in a very short time.
Please fill in your details.